有关自字符串和数组的一些基本算法
1.字符串匹配
- 从长度为n的母串中匹配长度为m的子串
- 两种算法
- 暴力匹配
- kmp
暴力匹配
- 顺序遍历母串,将每个字符作为匹配的起始字符,判断是否匹配子串,时间复杂度为:
O(m*n)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32int strMatch(const char* src, const char* target)
{
// 字符串不为空
if (!strlen(target) || !strlen(src))
{
return -1;
}
int index = 0;
while (index <= (strlen(src) - strlen(target)))
{
int count = 0;
bool flag = true;
while (count < strlen(target))
{
if (src[count+index] != target[count])
{
flag = false;
break;
}
count++;
}
if (flag)
{
return index;
}
index++;
}
return -1;
}
KMP 算法
- 参考1
- 参考2
- 时间复杂度:
O(m+n)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
void build_next_table(int *next, char *target_str) {
next[0] = 0;
int target_len = strlen(target_str);
// 遍历 target_str 的所有子串
for (int i = 1; i < target_len; ++i) {
// 前缀子串
std::set<std::string> head_set;
std::string tmp_head = "";
tmp_head = target_str[0];
head_set.insert(tmp_head);
for (int j = 1; j < i; ++j) {
tmp_head = tmp_head + target_str[j];
head_set.insert(tmp_head);
}
// 后缀子串
std::set<std::string> tail_set;
std::string tmp_tail = "";
tmp_tail = target_str[i];
tail_set.insert(tmp_tail);
for (int j = i - 1; j > 0; --j) {
tmp_tail = target_str[j] + tmp_tail;
tail_set.insert(tmp_tail);
}
// 共同子串的集合
std::set<std::string> common_set;
for (const auto &sub_str : head_set) {
if (tail_set.count(sub_str) > 0) {
common_set.insert(sub_str);
}
}
// 找出最长的共同子串
int max_len = 0;
for (const auto &common_str : common_set) {
if (common_str.size() > max_len) {
max_len = common_str.size();
}
}
next[i] = max_len;
}
}
int kmp(char *src_str, char *target_str) {
if (src_str == nullptr || target_str == nullptr) {
return -1;
}
int src_len = strlen(src_str);
int target_len = strlen(target_str);
int *next = new int[src_len];
build_next_table(next, target_str);
for (int i = 0; i< target_len;i++)
{
std::cout << next[i] << " ";
}
int cur_find = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < src_len;)
{
if (src_str[i] == target_str[cur_find])
{
i++;
cur_find++;
}
else
{
if (cur_find == 0)
{
++i;
}
else
{
cur_find = next[cur_find-1];
}
}
if(cur_find == target_len)
{
delete []next;
return i - target_len;
}
}
delete []next;
return -1;
}
通过hash解决字符串问题
- 有一些关于string的算法题目,例如:
- 判断两个string是否为各自的排列?
- 判断string中字符是否重复?
给一个int[]和一个int,数组中是否存在两个数之和为target?
- 暴力解法:先从数组中确定一个,再遍历其他的数,计算和是否为target -> O(n*n)
- 通过 hashtable解决,将
int[]转化成map[int]int,计算target-array[i]是否在map中 -> O(n)
给一个int[],找出最长连续的子数组?
- 例如:给你
[31,9,74,3,4,2,1,],返回[1,2,3,4] - 思路如下:
- 首先使用hash table去除重复元素
- 遍历 hash table,对于每一个元素x,如果 x-1 存在,则这个数必定不是最长的
- 然后对于 x-1 不存在的元素,依次搜索 x+n,记录长度
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
// longest slice in array
func maxSubString(src []int) int {
m := make(map[int]bool)
// delete repeated
for _, v := range src {
m[v] = true
}
longest := 0
for value := range m {
// not the longest
if _, isExist := m[value-1]; isExist {
continue
}
tempLongest := 0
for {
if _, isExist := m[value+tempLongest]; !isExist {
break
}
tempLongest++
}
if tempLongest > longest {
longest = tempLongest
}
}
return longest
}
给出两个字符串,返回最长的相同子串?
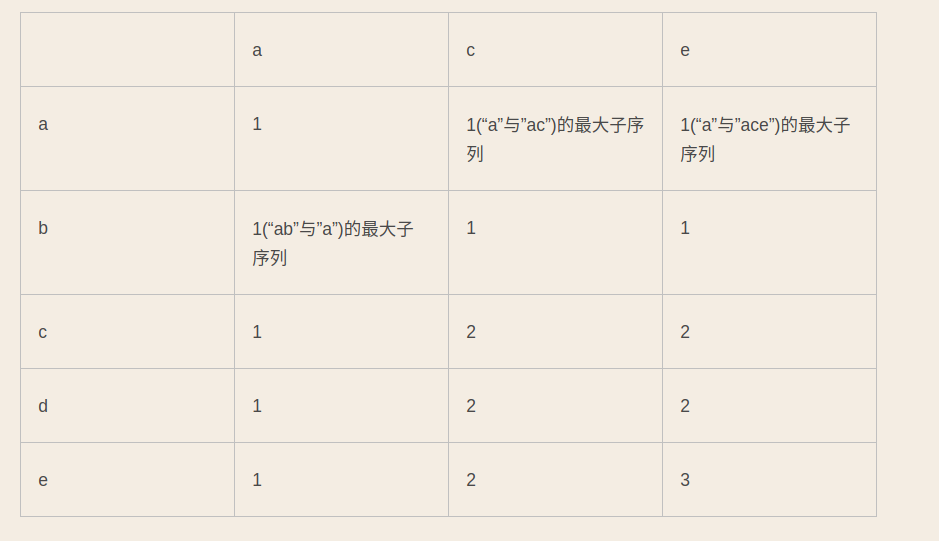
动态规划问题- 例如:s1=”abcde” s2= “ace”,求两个字符串的公共子序列,答案是“ace”
- S{s1,s2,s3….si} T{t1,t2,t3,t4….tj}
- 子问题划分
(1) 如果S的最后一位等于T的最后一位,则最大子序列就是{s1,s2,s3…si-1}和{t1,t2,t3…tj-1}的最大子序列+1
(2) 如果S的最后一位不等于T的最后一位,那么最大子序列就是① {s1,s2,s3..si}和 {t1,t2,t3...tj-1} 最大子序列 ② {s1,s2,s3...si-1}和{t1,t2,t3....tj} 最大子序列 - 以上两个自序列的最大值 - 边界
- 只剩下{s1}和{t1},如果相等就返回1,不等就返回0
- 使用一个表格来存储dp的结果
- 如果 S[i] == T[j] 则dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1
- 否则dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j-1],dp[i-1][j])
1 | func longestCommonSubsequence(text1 string, text2 string) int { |