centos7 上 systemd 详解
简介
CentOS 7继承了RHEL 7的新的特性,例如强大的systemd, 而systemd的使用也使得以往系统服务的/etc/init.d的启动脚本的方式就此改变, 也大幅提高了系统服务的运行效率。但服务的配置和以往也发生了极大的不同,同时变的简单而易用了许多。
CentOS 7的服务systemctl脚本存放在:/usr/lib/systemd/,有系统 system 和用户 user 之分, 即:/usr/lib/systemd/system 和 /usr/lib/systemd/user
配置文件
这里我们先要说明一下unit的文件位置,一般主要有三个目录:
1
2
3/lib/systemd/system
/run/systemd/system
/etc/systemd/system这三个目录的配置文件优先级依次从低到高,如果同一选项三个地方都配置了,优先级高的会覆盖优先级低的。 系统安装时,默认会将unit文件放在/lib/systemd/system目录。如果我们想要修改系统默认的配置,比如nginx.service,一般有两种方法:
- 在/etc/systemd/system目录下创建nginx.service文件,里面写上我们自己的配置。
- 在/etc/systemd/system下面创建nginx.service.d目录,在这个目录里面新建任何以.conf结尾的文件,然后写入我们自己的配置。推荐这种做法。
/run/systemd/system这个目录一般是进程在运行时动态创建unit文件的目录,一般很少修改,除非是修改程序运行时的一些参数时,即Session级别的,才在这里做修改。
服务配置
- 每一个服务以.service结尾,一般会分为3部分:[Unit]、[Service]和[Install],就以nginx为例吧,具体内容如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16[Unit]
Description=nginx - high performance web server
Documentation=http://nginx.org/en/docs/
After=network.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid
ExecStartPre=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID
ExecStop=/bin/kill -s QUIT $MAINPID
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
配置项说明
- 下面分别解释下着三部分的含义
[Unit]
- Description : 服务的简单描述
- Documentation : 服务文档
- After= : 依赖,仅当依赖的服务启动之后再启动自定义的服务单元
[Service]
- Type : 启动类型simple、forking、oneshot、notify、dbus
- Type=simple(默认值):systemd认为该服务将立即启动,服务进程不会fork。如果该服务要启动其他服务,不要使用此类型启动,除非该服务是socket激活型
- Type=forking:systemd认为当该服务进程fork,且父进程退出后服务启动成功。对于常规的守护进程(daemon),除非你确定此启动方式无法满足需求, 使用此类型启动即可。使用此启动类型应同时指定PIDFile=,以便systemd能够跟踪服务的主进程。
- Type=oneshot:这一选项适用于只执行一项任务、随后立即退出的服务。可能需要同时设置 RemainAfterExit=yes 使得 systemd 在服务进程退出之后仍然认为服务处于激活状态。
- Type=notify:与 Type=simple 相同,但约定服务会在就绪后向 systemd 发送一个信号,这一通知的实现由 libsystemd-daemon.so 提供
- Type=dbus:若以此方式启动,当指定的 BusName 出现在DBus系统总线上时,systemd认为服务就绪。
- PIDFile : pid文件路径
- Environment : 环境变量(可以添加多个)eg :Environment=REPO_REF=dev
- ExecStartPre :启动前要做什么,上文中是测试配置文件 -t
- ExecStart:启动
- ExecReload:重载
- ExecStop:停止
- PrivateTmp:True表示给服务分配独立的临时空间
[Install]
- WantedBy:服务安装的用户模式,从字面上看,就是想要使用这个服务的有是谁?上文中使用的是:multi-user.target ,就是指想要使用这个服务的目录是多用户。
操作示例
- 每一个.target实际上是链接到我们单位文件的集合,当我们执行
1
systemctl enable nginx.service
- 就会在 /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/ 目录下新建一个 /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service 文件的链接。
常用的service操作
1 | # 自启动 |
Systemd + Golang Demo
下面例子通过 Systemd 部署一个最简单的 Golang Web Server
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20package main
import (
"flag"
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
var address string
flag.StringVar(&address, "address", "5353", "listen address")
flag.Parse()
http.HandleFunc("/", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
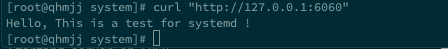
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello, This is a test for systemd !\n")
}) // 设置访问路由
log.Printf("Starting server on %s\n", address)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(fmt.Sprintf(":%s", address), nil))
}编译代码,并将可执行文件同步到远程服务器上
1
2
3CGO_ENABLED=0 GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 go build -o systemd-test main.go
rsync -zP ./systemd-test root@gp-aliyun:/usr/local/bin/在远程服务器上编写服务配置,放在/etc/systemd/system/中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11[Unit]
Description=Systemd Test
After=network.target
[Service]
User=nobody
# Execute `systemctl daemon-reload` after ExecStart= is changed.
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/systemd-test -address "6060"
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target通过systemctl启动服务
1
2
3
4
5
6
7# 每一次修改ExecStart都需执行
systemctl daemon-reload
# 启动
systemctl start systemd-test.service
# 查看状态
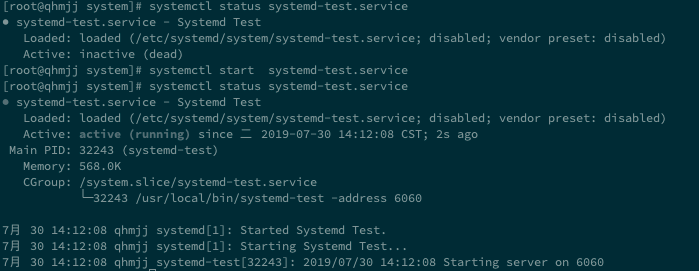
systemctl status systemd-test.service状态如下
可以通过curl进行测试: